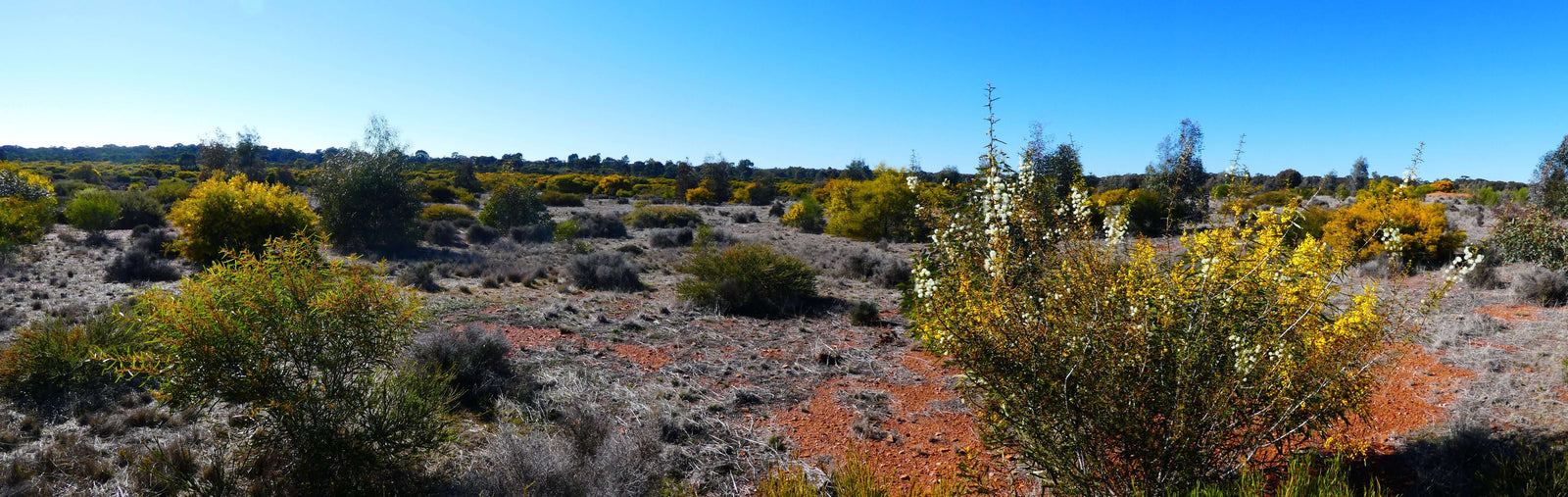
Avoca lies within Wiradjuri Country, north of Wagga Wagga in NSW. Greenfleet restored this native forest to deliver climate action and help support the area's significant biodiversity values.
In 2013, Greenfleet began revegetating the property, which had previously been used for wheat and canola cropping and sheep production. Further planting in 2017 enhanced our work at this site and Avoca is now a well-established native ecosystem.
Location & Map
The Avoca forest grows on the lands of the Wiradjuri people, adjacent to the Buddigower Nature Reserve. This Reserve and surrounds are recognised for its birdlife and is regularly used as a bird-banding site.
This is one of many native reforestation projects that Greenfleet has undertaken in New South Wales since 1997. To see where some of our other projects are growing, you can explore our forest map here.
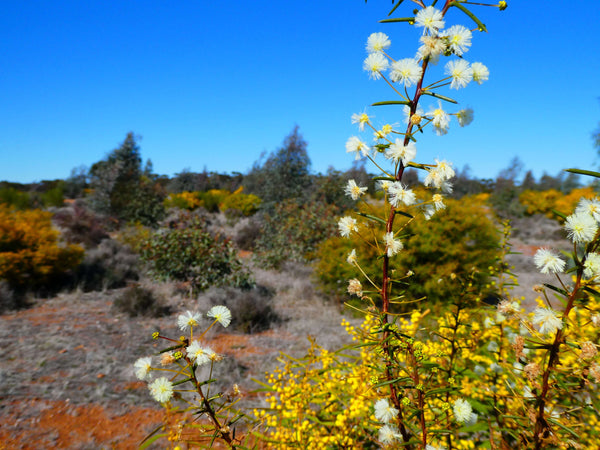

Revegetation Approach & Species Selection
The region surrounding Avoca has been extensively cleared for cropping and grazing, with remaining native vegetation in a highly fragmented state.
Buddigower Nature Reserve is one of only three NSW reserves containing the critically endangered “Mallee and Mallee-Broombush dominated woodland and shrubland”, as listed under the Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995 (NSW). It is situated within a bioregion very poorly represented in conservation areas.
By revegetating Avoca, Greenfleet is delivering climate action by removing carbon whilst also protecting and conserving the natural values of the region.
Preparation on the site began in 2013, with the seeding occurring in the winter months. A short 18 months later, most of the seeds had already germinated and grown into healthy native seedlings - some of them reaching over 1.5m in height!
This forest is extending the biological values of the nearby Buddigower Nature Reserve with Greenfleet planting of 977 hectares of protected habitat. This work is restoring the pre-clearing vegetation and creating habitat similar to that of the adjacent Reserve.
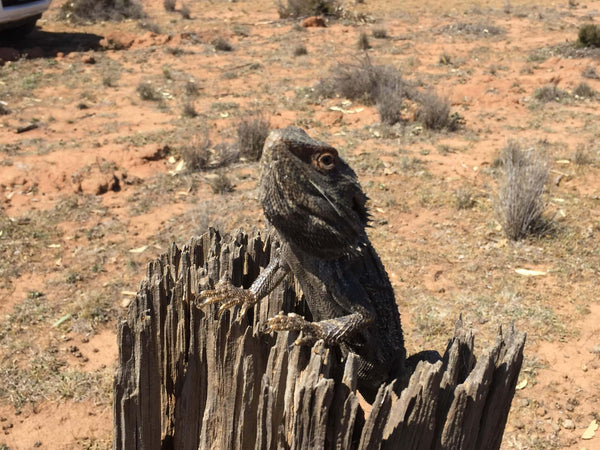

Wildlife Habitiat Restoration
As well as delivering climate action by removing carbon, the forest growing at Avoca is also restoring critical habitat for the region’s wildlife.
Prior to Greenfleet’s work at this site, over 200 native wildlife species were found on the reserve adjacent to our revegetation project at Avoca. These include birds such as the Shy Heathwren, Varied Sittella and Brown Treecreeper.
The tree and plant species restored at Avoca are providing potential food and habitat sources for species moving through the area. This includes habitat for threatened species, such as the endangered Swift Parrot on its winter migration.

Climate Action
The forest growing at Avoca is legally protected for 100 years. Over that time, it will remove over 345,000 tonnes of carbon from the atmosphere, which is the equivalent of what almost 80,300 average vehicles emit on Australia’s roads in a single year.
Location Size
Avoca is located just west of Alleena, 35 kilometres southwest of West Wyalong in New South Wales. The total property is 1,700 hectares, and Greenfleet revegetated 977 hectares to extend the forest on other parts of the property.
Planting Dates
2013 & 2017
Species
The revegetation project included the planting of
45 different native species. Here is a selection of the species sown:
- Acacia paradoxa
- Acacia doratoxylon
- Brachychiton populneus
- Cassinia laevis
- Eucalyptus dumosa
- Eucalyptus viridis
- Melaleuca uncinata




